




▶ Shared/Stolen data now remains protected
▶ Use Millions of keys to secure a database's fields/records
▶ Keys and data unite only for authorized users
▶ Data protection is only about securing data

The heart of Cy4Secure’s data protection is an 800-bit stream cipher algorithm. It is based on the industry hardened Mersenne Twister (MT) algorithm for its keystream. MT is commonly found and used in applications such as Microsoft’s Excel, Mathworks’ MatLab, Wolfram Research’s Mathematica, and development languages such as C++, GNU, PHP and Python. The National Security Agency (NSA) has used stream ciphers since the 1950s and it has many advantages. It can achieve a high security level with much less computational effort than the more common block ciphers. Stream cipher protected data is more difficult to attack because of the changing states and it is extremely fast. Another benefit is the detection of data corruption with encryption. Cy4Secure, when decrypting, constantly checks the integrity of the data and can flag when data has rotted. In other words, protected data is more secure and durable.
The next challenge in securing data is managing all the encryption keys used to protect data. Today, whether it is a simple password or a complex 800-bit key, users are forced to individually manage these keys to access data. Cy4Secure simplifies management by associating keys with the email address, common access control lists or active directories with whom protected data is shared. This can be a group of people, a distribution list, or a single individual. There are many benefits to this approach. Access to protected data is akin to already deployed access control list for the IT organization which is as simple as selecting recipients from a user’s contact list.
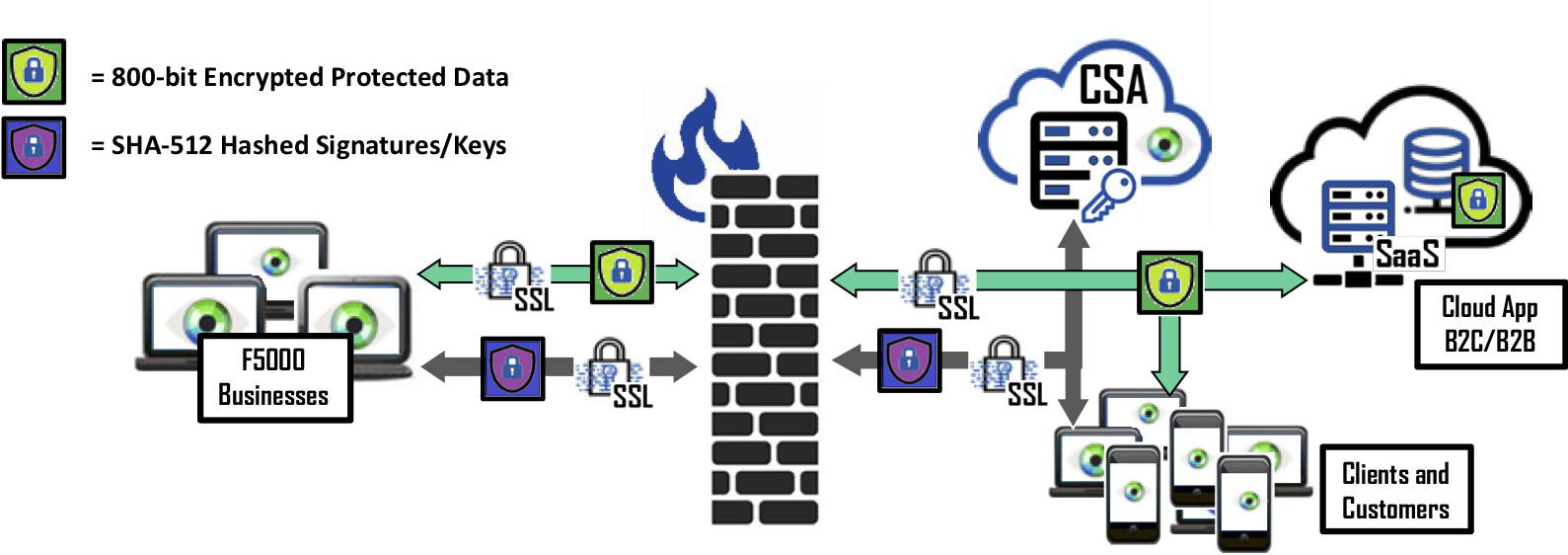
Once data is securely protected, key management is fully automated and transparent. Access can be easily controlled by the owner/sender, IT, or DevOps for shared data located on other servers, in the cloud, or on recipients’ computers. Availability of the decryption keys can be defined in many ways: When data can be first accessed, “Time to Birth”; How long it can be accessed, “Time to Live”; Or where it can be geographically accessed. Access permission can be revoked at any time. In the case when Cy4Secure protected data is lost, stolen, abandoned, or forgotten, it remains secure and becomes permanently inaccessible once access is removed or retired, ensuring cybercriminals or non-authorized users only obtain unintelligible data.


▶ Databases simply operate on Cy4Secure encrypted data
▶ Networks, applications, DBMSs remain unchanged
▶ No perceptible impact to performance
▶ Secure Data-In-Use operations

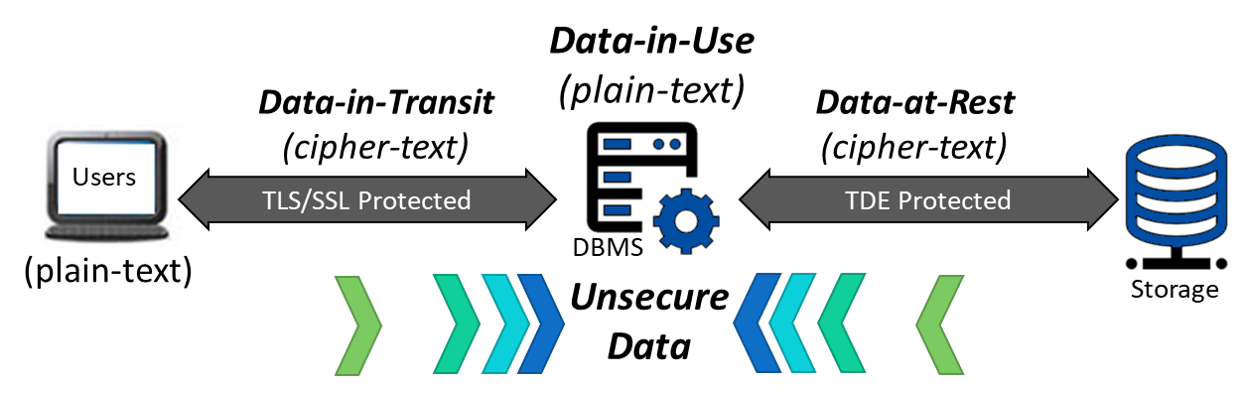
Bonafeyed‘s approach eliminates the tedious task of cryptography, encryption key management and access control is completely transparent to users or applications with the goal of protecting all data, data types and size of data no matter where it’s shared or how it is utilized. Bonafeyed’s Cy4Secure data security solution works behind the scenes such that all data is encrypted using 800-bit or 256-bit encryption just before sending to a database management system, database backed websites, SaaS or cloud applications. These applications simply use the protected data without knowing its encrypted. This is because it still appears as real data that can be searched, sorted, queried and referenced and databases do not know if the data is English, German, French, or Italian. In other words, Cy4Secure encrypted data appears as just another language.
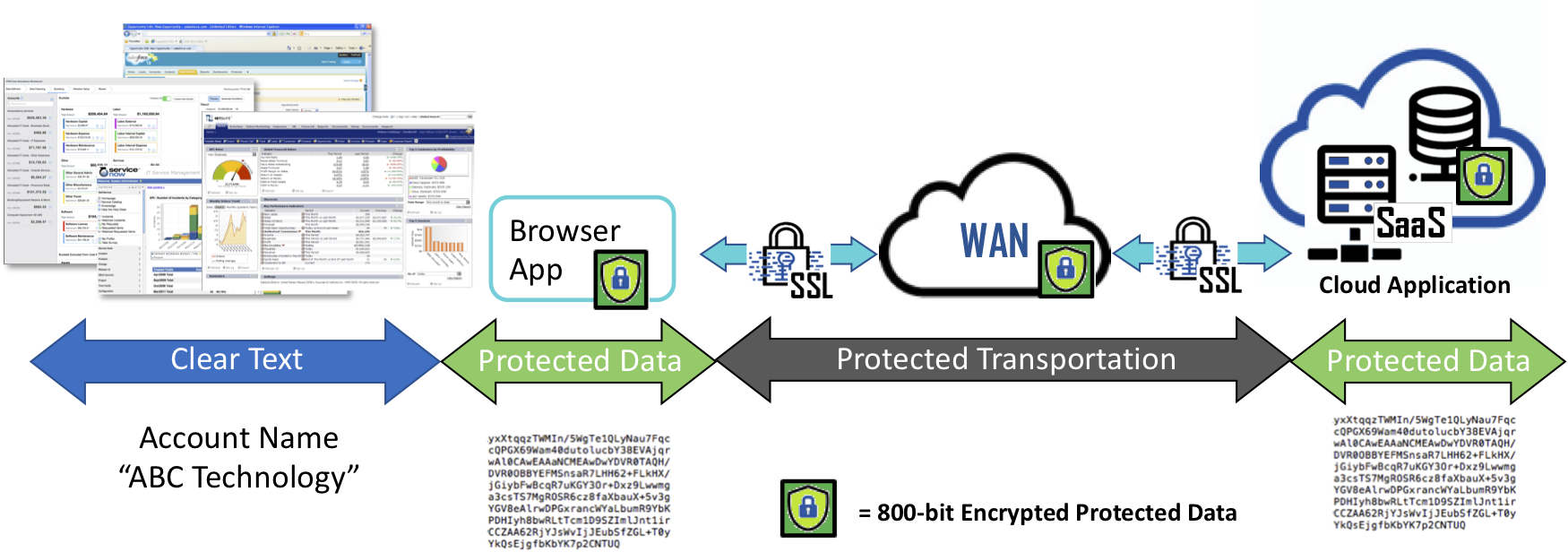
Cy4Secure data defined security works behind the scenes such that all data is encrypted using 800-bit or 256-bit keys just before sending to a database backed website, SaaS or cloud applications. In turn, when recipients receive Bonafeyed encrypted data and they are authorized, it is unencrypted without additional steps or separate passwords to gain access to the data. The “clear” data is also available for the user’s local application or web browser.
Eliminating the arduous task of data encryption now ensures the security of all data in-use by applications, or shared with others, remains in the control of the sender or data owner. When Bonafeyed protected data is lost, stolen, abandoned, or forgotten, it remains secure and becomes permanently inaccessible once access is removed or retired ensuring cybercriminals or non-authorized users only obtain unintelligible, demonetized data.


▶ Bonafeyed “Encrypted” data always remains secure
▶ Secures backups, server memory, and endpoint storage
▶ Cy4Secure is interoperable with all security schemes

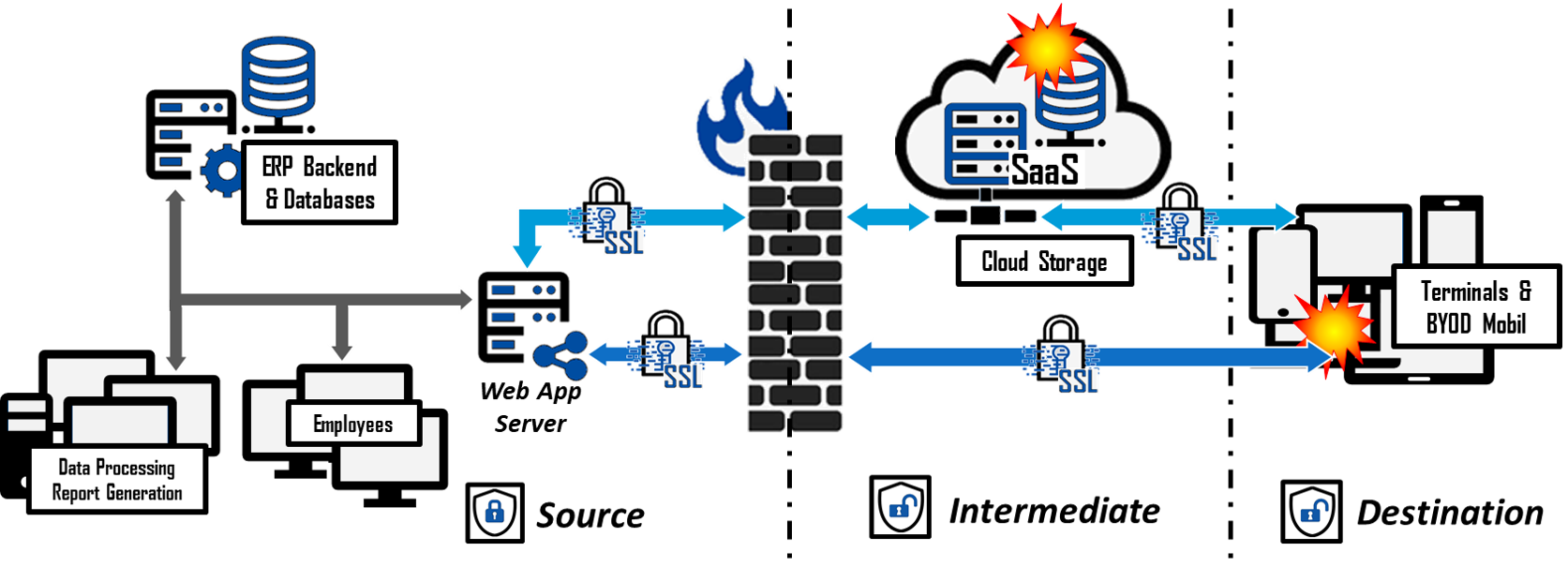
Cy4Secure introduces “data element security domain” where once data is encrypted, it remains secure and access can be controlled by the owner no matter where the data resides. Once this protected data is passed to intermediate applications/machines such as a web application server or a cloud compute instance, the data remains encrypted and unusable in the event of a breach. Upon arrival at the destination endpoint, the data remains encrypted until the recipient is authenticated by Cy4Secure as someone authorized by the data owner or application to access the data.
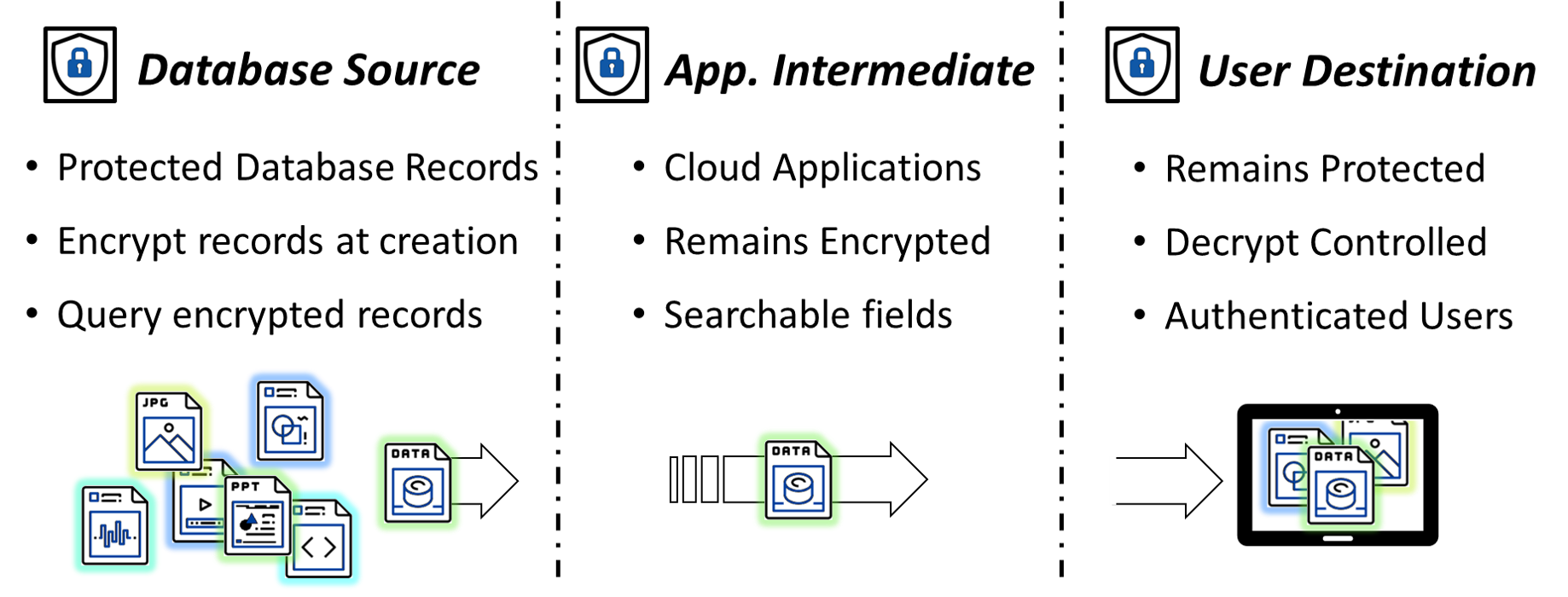
In the event data is stolen or intercepted, the Cy4Secure protected data remains secure. For example, when backing up a recipient’s machine, moving backups to an archive or cold tier, or forwarding the protected data to a co-worker or in the event a mobile device is stolen along with the protected data. In all cases, when Cy4Secure protected data is lost, stolen, abandoned, or forgotten, it remains secure and becomes permanently inaccessible once access is removed or retired, ensuring cybercriminals or non-authorized users only obtain unintelligible data.


▶ Application data paths are untouched
▶ Decentralized endpoint crypto operations
▶ CSA scales to trillions of keys and millions of users
▶ No bump-on-wire or data bottlenecks

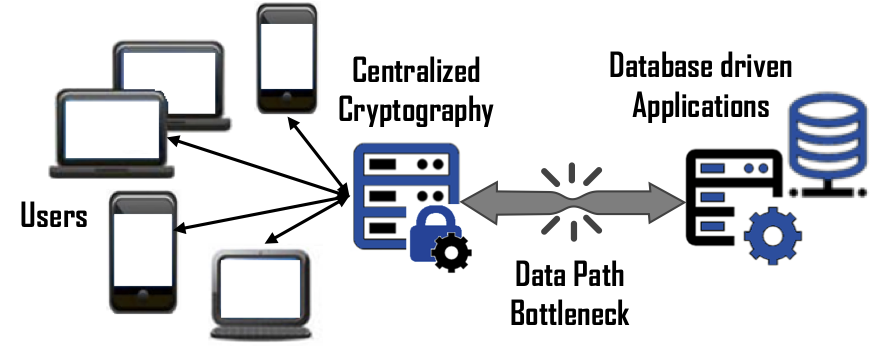 Scalability – In a large-scale data protection solution, many companies will design a solution such that all users must connect to a centralized function that is a proxy for the application it is protecting. Unfortunately, this also means the appliance, servlet or instance is responsible of encrypting and decrypting the requests, managing cryptographic keys, and providing authorization for 100’s to 1000’s of users along with funneling petabytes of data to and from the protected application. Bonafeyed’s approach splits the data path from the other functions so that each user connects to the database driven application separately and performs the cryptographic operation on the user’s endpoint device. With this, there are no data path bottlenecks and the massive amount of computing resources in the hands of the user is effectively utilized. This means an already deployed system can continue to support that same number of simultaneous users on the protected database back application.
Scalability – In a large-scale data protection solution, many companies will design a solution such that all users must connect to a centralized function that is a proxy for the application it is protecting. Unfortunately, this also means the appliance, servlet or instance is responsible of encrypting and decrypting the requests, managing cryptographic keys, and providing authorization for 100’s to 1000’s of users along with funneling petabytes of data to and from the protected application. Bonafeyed’s approach splits the data path from the other functions so that each user connects to the database driven application separately and performs the cryptographic operation on the user’s endpoint device. With this, there are no data path bottlenecks and the massive amount of computing resources in the hands of the user is effectively utilized. This means an already deployed system can continue to support that same number of simultaneous users on the protected database back application.
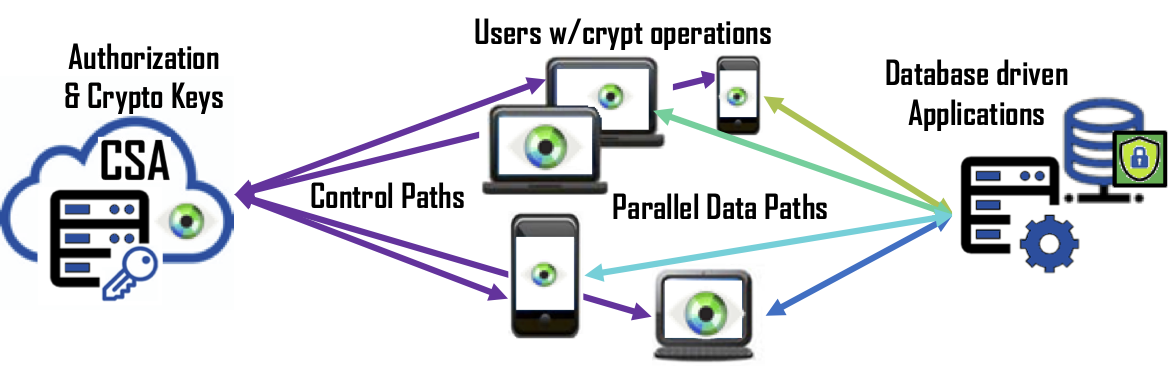
Performance – User experience is key to deploying a data security solution. Slower response from a database or application sluggishness due to the overhead of data protection will frustrate users and impact businesses. Cryptographic operations can be computationally intensive, thus slowing application response. Natively turning on Columnar Level Encryption (CLE) on a database, for example, can impact query performance from 20-30% for a single column of data. Bonafeyed performs the encryption/decryption operations on the endpoint devices such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, and terminals which have the capacity to decrypt data in real time and on-demand. Bonafeyed offers AES-256 and an extremely fast 800-bit stream cipher that is about 10 times faster and about double the encryption strength. This translates into little to no impact on an application or user experience when data is being encrypted or decrypted.
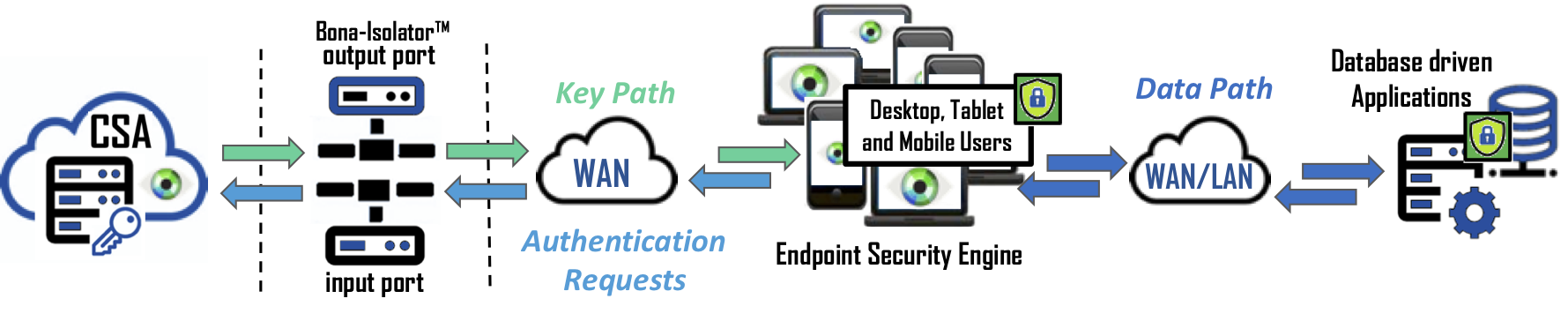
Data Security – The strongest data security approach is to never bring encryption keys together with data until it is authorized and on the end user’s machine. Bonafeyed uses millions of keys to protect a database but only retrieves those keys needed to decrypt a user’s data on their end-point device. Keys are protected behind the Cy4Secure’s air-gap technology, and only recently used keys are present on end-point devices limiting exposure in order to protect the data.


▶ Select any combination of predicates and conditions
▶ Fully compatible with search engines
▶ Search structured and unstructured data fields
▶ Works with all Database Management Systems

To accomplish this feat, data records are encrypted when entered or updated in a database. DBAs and the Chief Data Officers or CISOs can define the encryption schema for each data field, row, or column using common or different 800-bit or 256-bit encryption keys. Each column can either be encrypted for order preservation or equality search ability, referred to as Column Level Encryption (CLE). Or to protect PHI and PII data fields such as social security numbers, credit card numbers or bank account information, a unique key can be used for each entry for maximum security and is not searchable. This is known as Field Level Encryption (FLE). In addition to innate data protection, a third level of protection is Row Level Encryption (RLE). RLE uses a common key for fields in the same row or record for exact match only searches and provides a legitimate multi-tenant database “row level security”. When combined, Bonafeyed brings a new level of data security that utilizes millions of keys to secure millions of data elements rather than just 1. Yes, millions to secure the contents within a database. This means every field, column or row can be encrypted, requiring many keys to decrypt a single record. Refer to Exceed Privacy Regulations to see how this fine-grain data protection is applied to individual PII and PHI data elements.
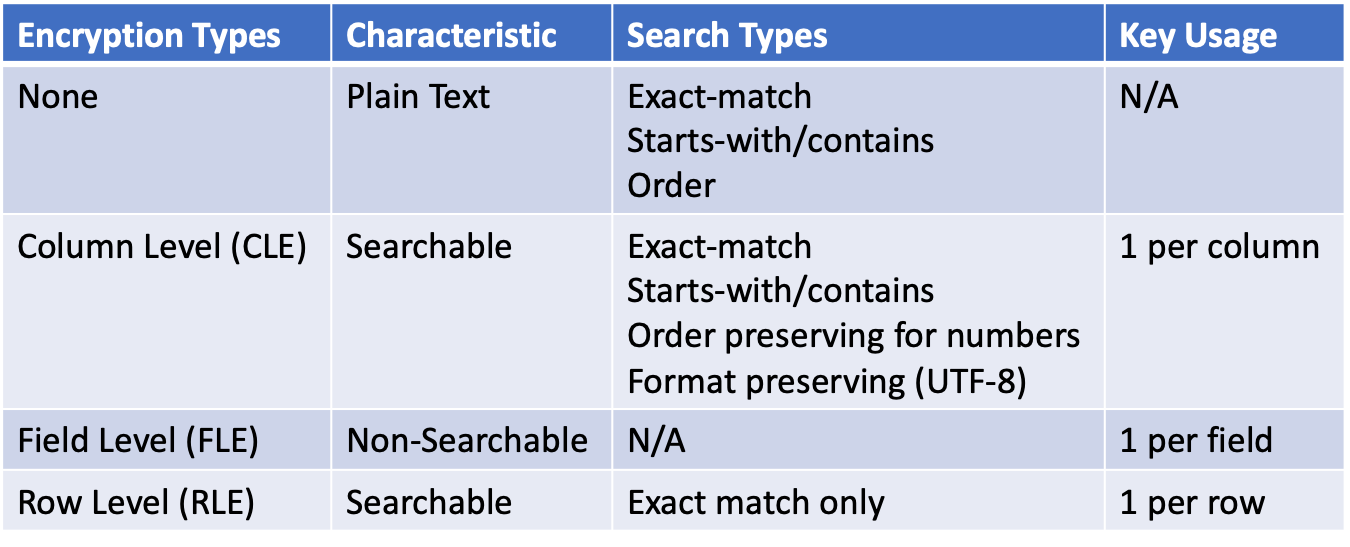
It turns out, a database does not know the difference between data that is encrypted with Cy4Secure or data that is human readable. Its only concern is that it meets the requirements of the field entry. Databases, storing Cy4Secure protected data, can still perform normal operations such as whole searches, partial searches, and groupings. When making queries, the search criteria is encrypted by Cy4Secure at the client and the database executes the query on the encrypted equivalent version of the data for exact match, starts-with, contains, ordered, or ranged. To make this possible, Cy4Secure ensures encrypted data continues to appear as data. Cy4Secure does not impose a specific encrypted data structure prior to sending other than providing the option of generating binary ASCII or hexadecimal output of the encrypted data. Otherwise, encrypted data appears as homogenized group of 1’s and 0’s, or unprintable characters not readily useable by an application. The data can simply be stored directly or with a tag identifying the utilized encryption key. The latter example affords a mixture of both encrypted and non-encrypted data in the same data set. A fast checksum verifies the data is encrypted and can be subsequently (after retrieving a key) decrypted prior to display or use.
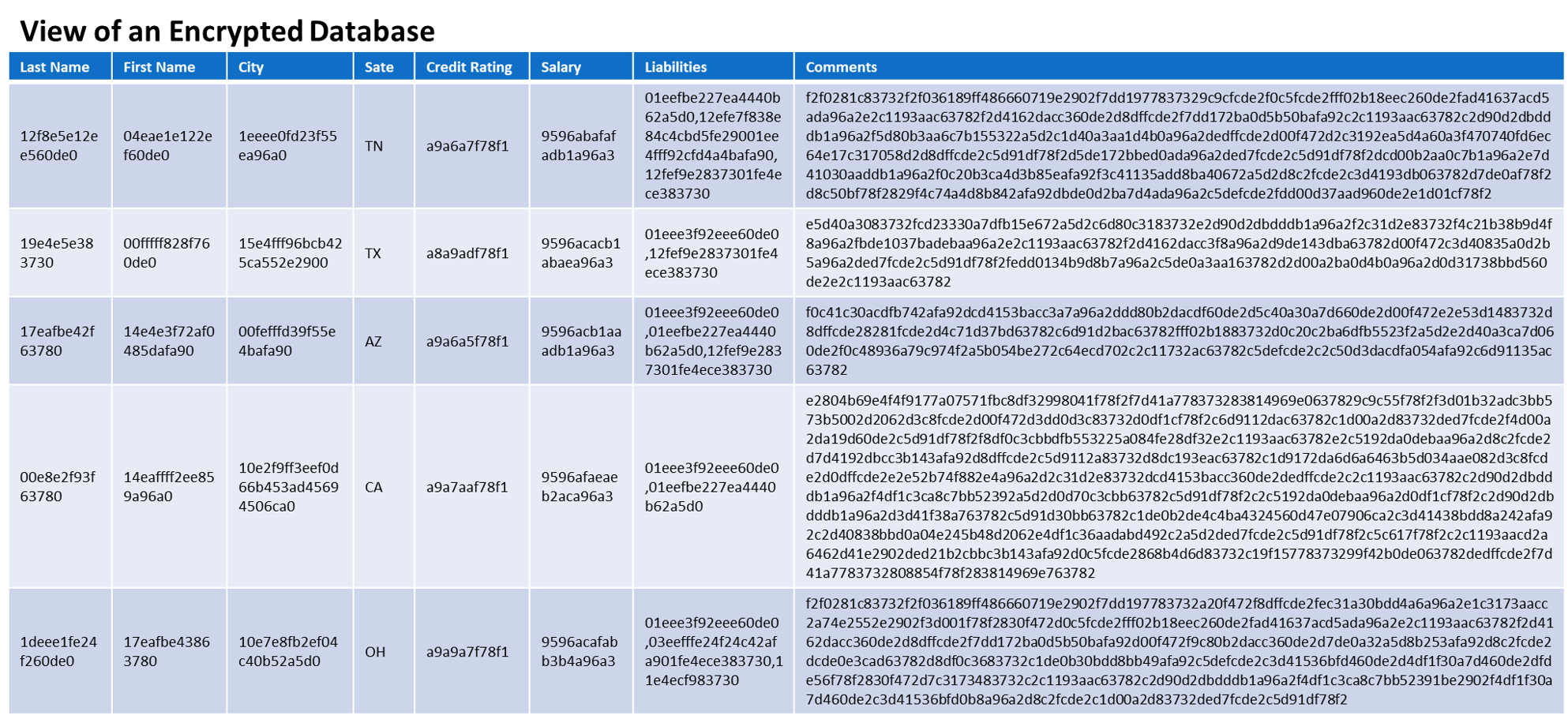
In the simplest description, a search is a search. That is, any Cy4Secure encryption operation performed during data entry can likewise be performed on any search criteria. Common grouped and cross-tabulated results can be performed on Cy4Secure encrypted data with the added benefit of generating reports with encrypted data that is only viewable by authorized persons. Deploying Bonafeyed’s Cy4Secure on database applications ensures the data fields within a database are encrypted and only accessible by authorized users. In the event of a breach, the data remains secured and private from cybercriminals or in-network non-authorized users.


