



▶ Lost business is about half the cost of a data breach
▶ Encrypted data has no value to the cyberthieves
▶ It takes millions of keys to open a protected database
▶ Over 300M people impacted by data breaches in 2020

In the case of a ransomware attack, the cybercriminal usually holds hostage the victim’s data for cryptocurrency, promising that once payment is made, they will re-enable access to the data with no guarantees of leaking it. Unfortunately, most of the time, adding insult to injury, cybercriminals not only collect the payment from the victim, but they also place the data on the dark web for the highest bidder. Imagine this being Personal Health Information (PHI). Whoever buys this data can now use it to extort anyone, even a high-profile target like an executive, celebrity or political figure, or worse yet, collect massive amounts of money via fraudulent insurance schemes using patients’ medical reports. Since Bonafeyed focuses solely on protecting the data, even when a cybercriminal hits the jackpot and stumbles into a wide-open database with millions of PHI records, the individual data fields and records remain encrypted requiring multiple keys to access a single record and millions of encryption keys to reveal the entire database.
Now consider another scenario that lately has been breaking many headline news – a cyberattack coming from an organized crime gang with affiliation to an unfriendly country. Today, we are witnessing more cases mentioning the FBI and other agencies helping companies resolve the problem with mixed results. Talk about a serious hostage situation! A quick pay-out to the criminals to get your business back is no longer a valid option and companies are stopped dead on their tracks, causing major headaches due to impact on operations and revenue. Relying on the reaction time of an overworked government agency to assist in the process for paying out the ransom, if allowed, should not be the only option.
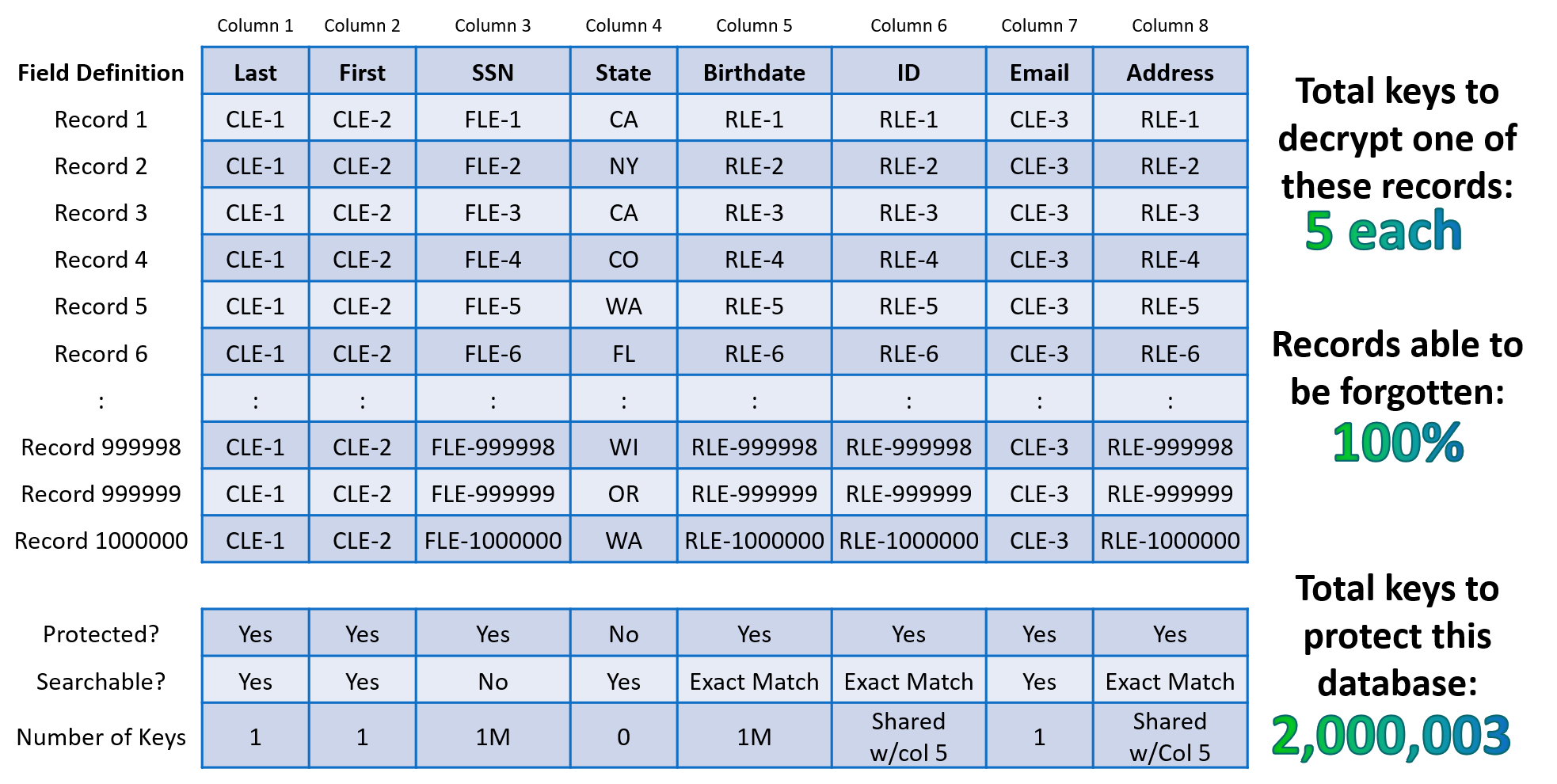
When Cy4Secure protected data is lost, stolen, abandoned, or forgotten, it remains secure and becomes permanently inaccessible once access to the encryption keys are removed or retired ensuring cybercriminals or non-authorized users only obtain unintelligible digital data.


